Contents at a glance
- Introduction to Beginner Workout
- What should beginners focus on?
- The fundamentals
- Get your goals straight
- How to lay the foundations?
- Structuring the workout
- Other antagonistic pairs
- Workout Routine for Beginners
- Circuit (Full-Body) Workout # 1
- Circuit (Full-Body) Workout # 2
- Exercise showcase – Circuit (Full-Body) workout #1
- Exercise showcase – Circuit (Full-Body) workout #2
Introduction To Beginner Workout
Everybody, at some point of their lives, decides to take care of their physical well-being. If you have stumbled upon our website, and this beginner workout routine, you are one step closer to being able to properly maintain your bodily temple!
The problem is when most of you have decided to take action, have no idea where to start and how to do it. Many, end up doing the wrong way without any form of guidance and in the process, injure themselves! The worst possible thing to happen is suffer from a permanent injury!
Thankfully our team of professionally trained fitness instructors from Mean Muscles have decided to create an actionable platform, that will help you quickly understand what approach to choose towards your training and even nutrition.
Besides the actionable workouts that you can see on our website (Which of course vary from beginner workout plans, to more advanced ones) you can also find a lot of valuable information in our section called “The Science“.
This is where we have all the educational content, including training and physiological principles and definitions. We personally do recommend you to go through this section and educate yourself when you have the time. Getting the ‘I know all that stuff’ will be always an advantage for you.
Now without further ado, let’s get to the essence of this.
(If you are really impatient to see the workout itself, you can scroll down and skip all the useful information before the workout table)
What Should Beginners Focus On?
Most beginners get into training with a wrong mind set, such as “I’ll just reduce this belly fat” or “I’ll just do crunches so I can get some abdominal definition” or even “I’ll just do arms every other day because 17-inch guns is the goal I’m chasing”
Well, the story is quite different, you will get chiseled abs and guns, but not the right away.
As a beginner, there’s this fundamental part that you need to first take care of, before being able to actually make significant, long-term progress.
The Fundamentals
Before you move on to goal-specific workout routines, there are a couple of things that you need to take care of first:
- Develop basic physical properties- Strength, strength endurance, cardio endurance
- Learn the correct execution of all basic exercises
- Get used to certain nutritional and sleeping habits
Doing that, you will lay a foundation, which will be your perfect starting point and environment for the body to progress furthermore.
Another thing you need to understand is that the body is capable of much more than you think it is. It is not just about losing or reducing that stubborn belly fat, or making your arms bigger. The body is a complex machine, that is capable of amazing feats of strength, beauty and athleticism.
And when you train correctly for a prolonged period of time, you will be able to develop an overall functional, beautiful, strong piece of art that can practically serve you and make you feel good throughout your entire life.
So, Step One- Get Your Goals Straight
Instead of “I just want to be fit in 4 weeks” set your goal to be “I want to experience the full-on beauty and strength of which my body is capable”.
After all, you can reduce fat quickly with fasting, but that will just lead your body to a state of constant exhaustion.
Instead, understand that you can make use of all your physical properties- You can look good, feel good and be a functional human being that can sprint, swim, jump, crawl and lift heavy things against the force of gravity any day, any time.
How To Lay The Foundations?
You can start off with any type of training, but we as personal trainers from MeanMuscles, focus on the most efficient type of training, according to the force of gravity, namely- Weightlifting.
Just a note here- Lifting weights is the most efficient type of training, simply because the body needs more and new tension to which it can adapt and grow and using actual weights is the best way to expose the body to new tension.
Also, select the proper time of the day for your workout sessions. If you work out in the morning, then you have to follow that routine for the following weeks.
You can take a look at some of the related articles on our website
So, is the perfect beginner workout routine “Chest-biceps, Back-triceps, etc.”?
Well, not really.
In order for you to be able to get used to the movement patterns of all basic exercises, it is recommended that you do an all-around, full-body circuit routine.
Structuring The Workout
The order of the muscle groups in the workout that we are about to show you is antagonistic.
What is the antagonistic order?
Antagonistic may sound like something straight out of the communism, but this is what antagonistic muscle groups actually are: Two muscle groups that are placed opposite to one another and have opposite functions.
Examples: Biceps and triceps- The biceps are flexors, while its antagonist, the triceps, are located right behind the biceps and have the opposite function of an extensor.
Other Antagonistic Pairs
Chest-Back
Quadriceps-Hamstrings
Abdominals-Lower back
Calves-Shins
Shoulders do not have an antagonistic, opposing muscle group.
Now that we know what antagonistic pairs are, here is the exact order of the workout according to the muscle groups:
Chest, back, shoulders, biceps, triceps, quadriceps, hamstrings, calves, abs, lower back.
Workout Routine For Beginners
The exercises, numbers of sets, numbers of repetitions and weights used.
Now, there’s a lot of discussion going on about the correct numbers of sets and repetitions, as well as weights used, but we will give you the correct information right away- It depends on the goal, the workout structure, where you are doing it, and the individual!
Working out at home can be challenging than a workout routine in a gym, so it is important to take it slow.
Every body reacts differently to the different ranges of repetitions and weights, but there are a couple of generic rules to follow when you want to build muscle:
- If you want to build muscle mass, you should be within the 70-85% range of your maximum capabilities, when it comes to the weights used. Your maximum capabilities are the weight that you can lift for a given exercise ONCE. Now, as a starter, it is not recommended for you to do heavy One-repetition-maximum lifts, so instead, finding your 70-85% is done by finding out the weight that gives you a challenge around the 8th repetition.
So, the conclusion to point number one- Building muscle mass requires 8 to 10 repetitions, that will give you a challenge, for the upper body, and 10-15 repetitions with a lower weight for the lower body.
It is important to remember that the lower body requires more VOLUME to grow, due to the fact it consists of bigger muscle groups (Quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, compared to biceps, triceps, shoulders which are significantly smaller in size).
Upper body- 8-12 repetitions with a challenging weight
Lower body- 10-15 repetitions with a challenging weight
- The second must of muscle building is completing the exercise with correct form. So, before focusing on weights that will give you a challenge, start off with really low weights, that will let you learn how to correctly do each exercise. (Don’t worry, in this article we will give you showcase and description of each exercise included in the workout routine for beginners) Only then you can focus on increasing the weights, while still keeping good form throughout the whole amplitude of the movement.
- The last but not least important rule of efficient training is recovery- You cannot hit arms every day and expect them to grow. After a workout, the musculature gets into a state of recovery. While recovering the energetic structures and damaged muscle fibers, the trained musculature reaches the point of hyper-recovery after about 48~72 hours (Depending on how heavy the workout was), which, is the perfect time to train the musculature again, so that it will be in a constant state of recovery and hyper-recovery, without having a window of inactivity.
So, as a beginner, the day-to-day workout regimen can be structured like this.
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weights | Rest, cardio | Rest, stretching | Weights, cardio | Rest, stretching | Weights | Rest, stretching |
In reality, with this type of weekly schedule you have 3 weight lifting workouts per week, along with 2 cardio sessions and 3 stretching sessions.
During the weight lifting workouts in the gym, you will be learning exercises, while also developing your strength and strength endurance.
On the cardio days, you will be resting from the weights, while working on your cardio endurance (We will talk about how to do your cardio later on in the article) and on the rest of the days, you will be working on your flexibility.
Now that we have created a proper weekly schedule, that will be your plan towards development, we can get to the workouts.
Below, we will present to you a couple of full-body workouts, which are built according to the antagonistic scheme, but consist of different exercises.
You can switch up between the two workouts on your different weight lifting days
Circuit (Full-body) Workout #1
Legend:
P-Primarily involved muscle groups
S-Secondarily involved muscle groups
| Exercise | Number of sets | Number of repetitions | Muscle groups involved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dumbbell flat bench press | 5 | 15,12,10,8,6 | P– Chest
S– Shoulders, triceps |
| Lat pulldowns | 5 | 15,12,10,8,6 | P– Back musculature
S– Biceps, forearms |
| Dumbbell shoulder press | 4 | 10 | P-Shoulders
S–Triceps |
| Alternate Dumbbell bicep curls | 3 | 10,10,8 | P– Biceps, forearms |
| Triceps bench dips | 3 | 12 | P– Triceps
S– Chest, shoulders |
| Bodyweight squats | 6 | 15 | P– Quadriceps
S-Hamstrings, glutes |
| Lying hamstring curls | 4 | 12 | P– Hamstrings |
| Standing calf raises | 5 | 15 | P– Calves |
| Crunches | 5 | Until failure | P– Abdominals |
| Lower back hyperextension | 5 | 15 | P– Lower back musculature |
Circuit (Full-Body) Workout #2
| Exercise | Number of sets | Number of repetitions | Muscle groups involved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incline barbell bench press | 5 | 15,12,10,8,6 | P– Upper chest
S– Shoulders, triceps |
| Cable rows | 5 | 15,12,10,8,6 | P– Back musculature
S– Biceps, forearms |
| Dumbbell lateral raise | 4 | 10,10,8,8 | P– Side deltoids
S– Whole shoulder contracts at the top of the movement |
| Z-Bar bicep curls | 3 | 12 | P– Biceps
S– Forearms |
| Overhead dumbbell tricep extensions | 4 | 10 | P– Triceps
|
| Hack squat | 5 | 15 | P– Quadriceps
S– Hamstrings, glutes |
| Leg press | 3 | 12 | P– Quadriceps
S– Hamstrings |
| Standing calf raises | 5 | 12 | P– Calves
S– Hamstrings |
| Seated calf machine raises | 3 | 15 | P– Calves |
| Lower back hyperextension | 4 | 12 | P– Spinal erectors |
Exercise showcase – Circuit (Full-Body) Workout #1
Dumbbell flat bench press
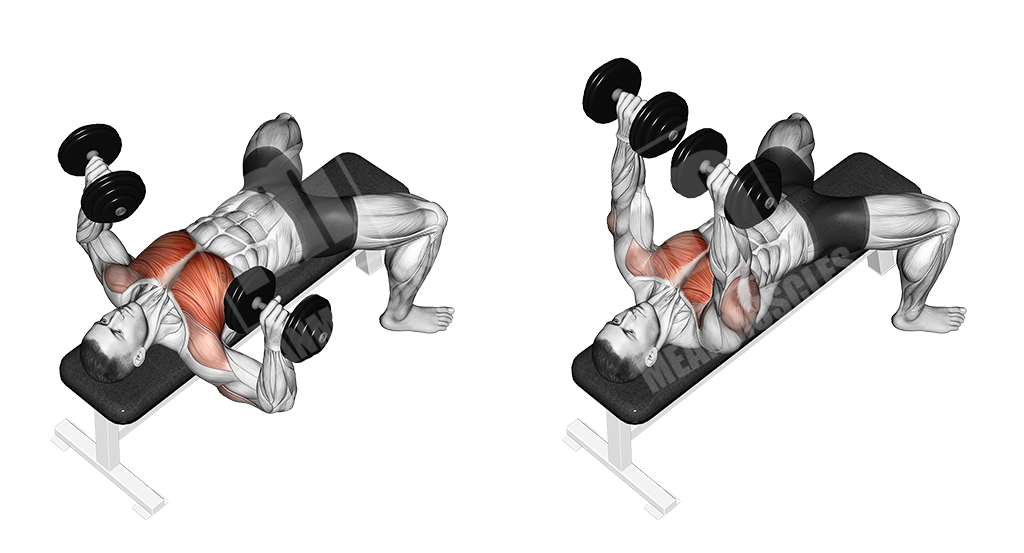

One of the basic dumbbell movements for the upper body, that primarily targets the chest muscles, while the triceps and shoulders work as synergists.
Execution
- Choose an appropriate weight
- Sit on the bench and put the dumbbells on your legs
- Lay on your back with your arms extended (Elbows slightly are slightly bent- Do not lock out)
- Let the dumbbells down to the lower portion of your chest
- Push the dumbbells up to the original position (Again, do not lock the elbows out)
Lat pull-downs
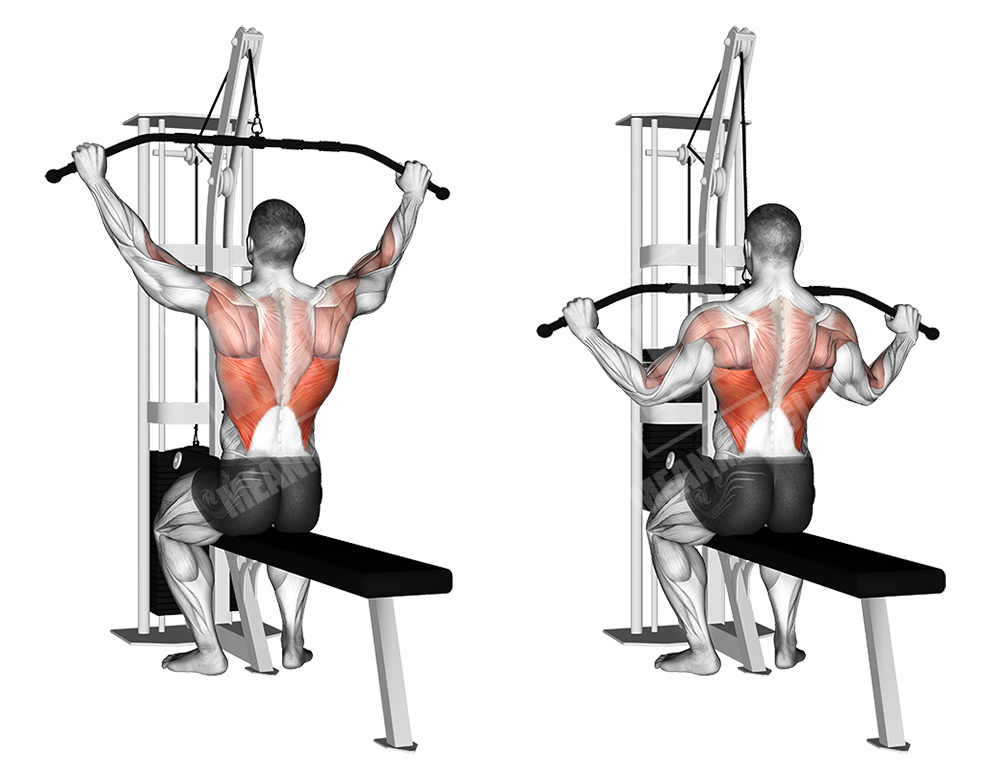

This cable exercise mimics the pull-up movement, with the only difference being it is done on a machine, so the body is in a fixed position.
Execution
- Grab the bar as wide as possible
- Sit down and tuck your legs under the pads
- Keep your chest puffed and your back muscles tensed
- Pull the bar down to the lower portion of the chest
- Return to the initial position and stretch out the back
- Proceed to the next rep
Dumbbell shoulder press
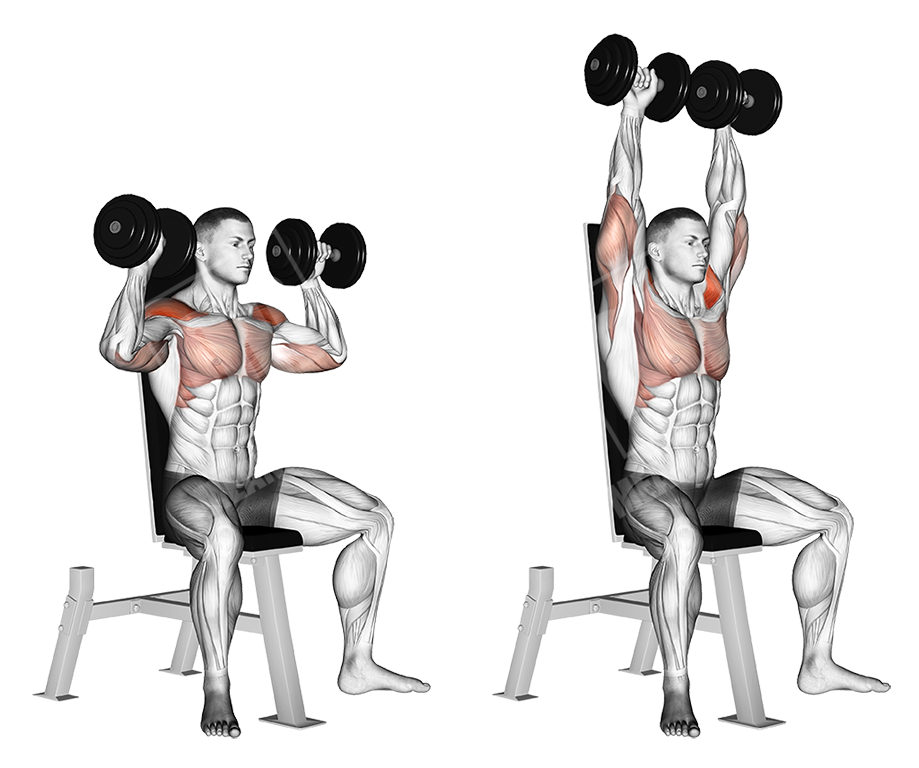

This is a basic pushing movement that targets the deltoids, mainly engaging the front part of them.
Execution
- Set the backrest of the bench to a 90-degree angle
- Choose an appropriate weight and sit down on the bench with the dumbbells on your legs and back rested.
- Push the dumbbells up so that your arms are at a 90-degree angle and the sides of the dumbbells are besides the sides of your head
- Push the dumbbells up as illustrated
- Let the dumbbells down and return to the initial position
Alternate Dumbbell Bicep Curls
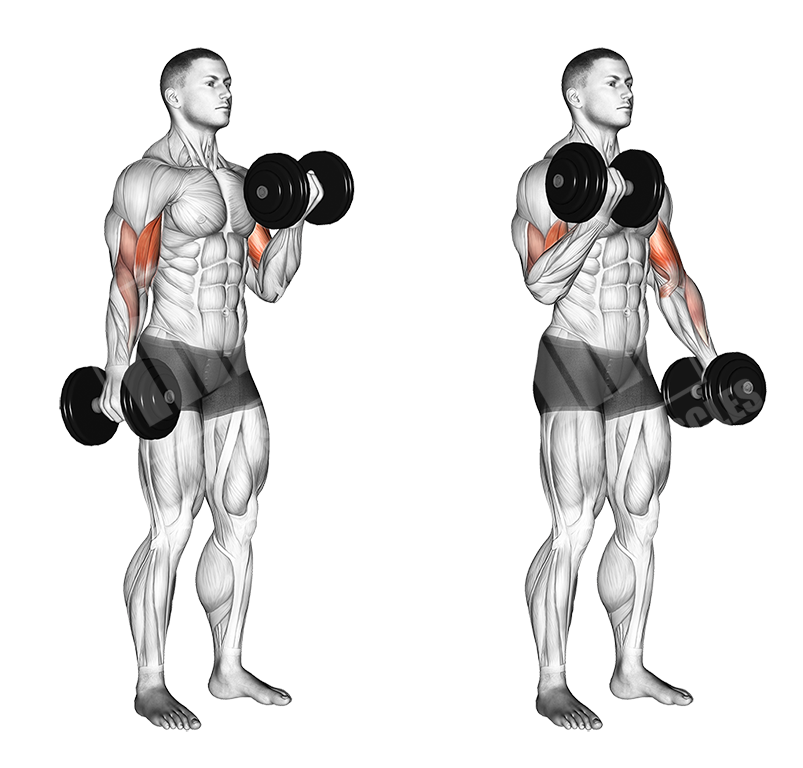


This basic dumbbell exercise allows you to separately use each arm. Unlike the barbell bicep curl, you can make use of the wrist supination, which will allow you to target the “Bicep peak” more.
Execution
- Choose an appropriate weight
- Keep the dumbbells by your side
- Curl the dumbbell on one side, supinating your wrist so that the pinky is pointing outwards
- Let the dumbbell down (optionally, contract the triceps)
- Proceed to the next rep on the opposite arm
Triceps Bench Dip
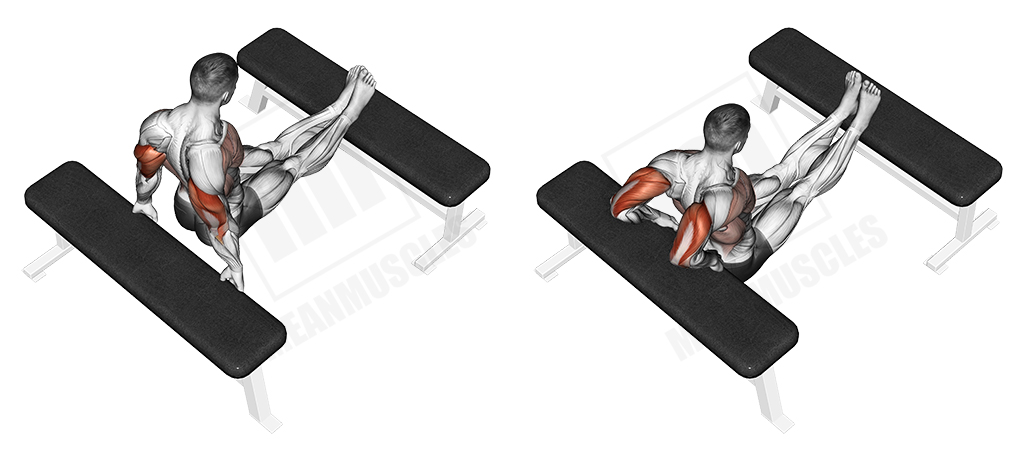

This body-weight exercise primarily targets the triceps and secondarily the chest and shoulders. It is done on a bench and the legs can either stay on the ground, or be lifted up on another bench, which will allow you to use your full body-weight.
Execution
- Sit on the side of a bench with your hands by your side
- Place your legs on another bench as illustrated
- Lift your torso so that you are on your arms only
- Let your body down until your upper arm is parallel to the ground
- Push yourself up, contracting your triceps
Note
Keep a moderate pace and don’t aggressively lock out the elbow.
Body-Weight Squats
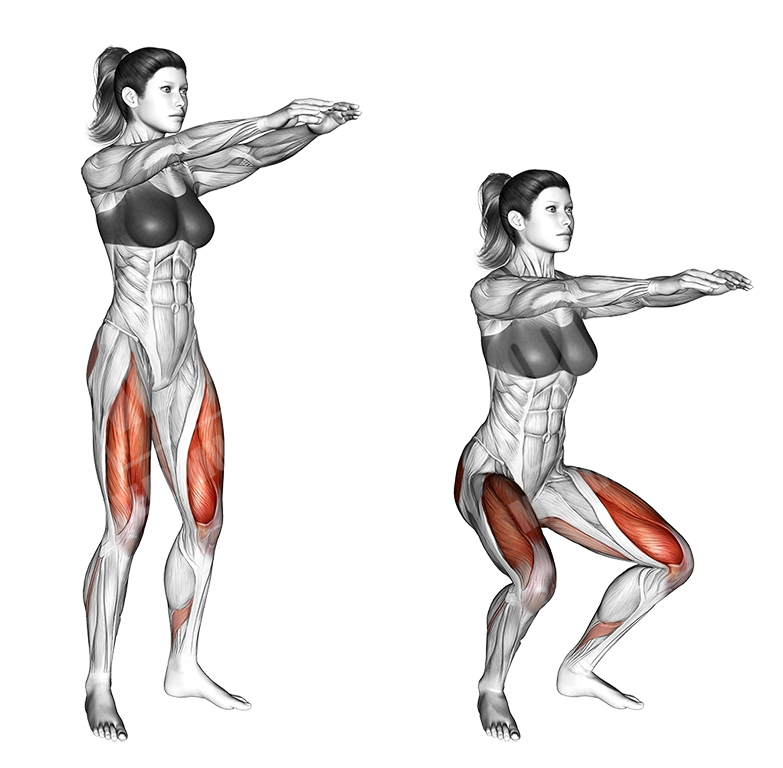

This basic body-weight exercise will help you build up strength in the lower body and learn how the basic squat movement works from a bio-mechanical point of view.
This will later on ease you on the exercise “barbell squat”.
Execution
- Stand with your feet at shoulder width or slightly wider
- Keep your toes pointing slightly outward
- Place your hands on your shoulders
- Let your body down, while keeping your back straight
- Squat down until the hamstrings are parallel to the ground (you can go lower if you wish to)
- Go all the way up to the initial position, without locking your knees out
Notes
Drive the tension through the heels.
You can optionally elevate your heels on two disks.
Lying Hamstring Curls
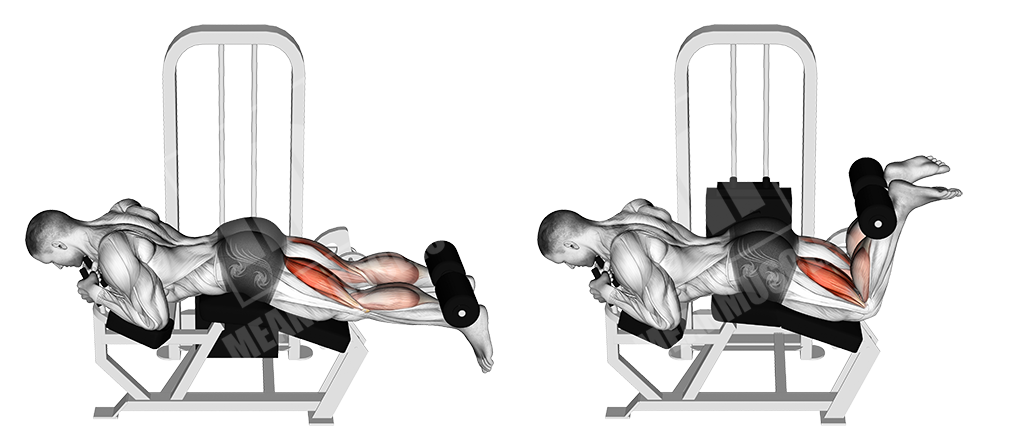

This is a basic machine exercise that isolates the biceps femoris (hamstrings).
Execution
- Lay face down and grab the handles
- Place your heels under the pads
- Keep the tension on your hamstrings and contract them via a curling motion
Standing Barbell Calf Raise
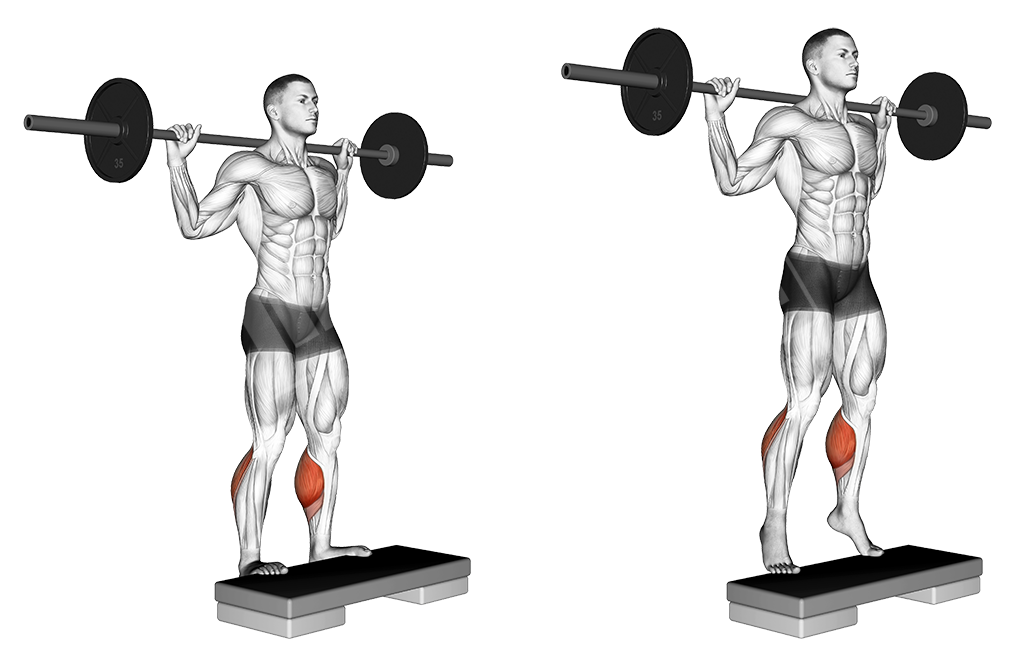

This is one of the best calf movements, as doing a calf raise with straight legs allows you to better engage the two heads of the calf musculature.
This exercise can be done with a barbell or on a smith machine.
Execution
- Get the bar on your trapezius so that you are comfortable
- Place your hands at shoulder width or slightly wider
- Step with your toes on a ledge
- Lift yourself up on your toes, contracting the calves
- Hold the contraction and return to the initial position
Floor Crunch
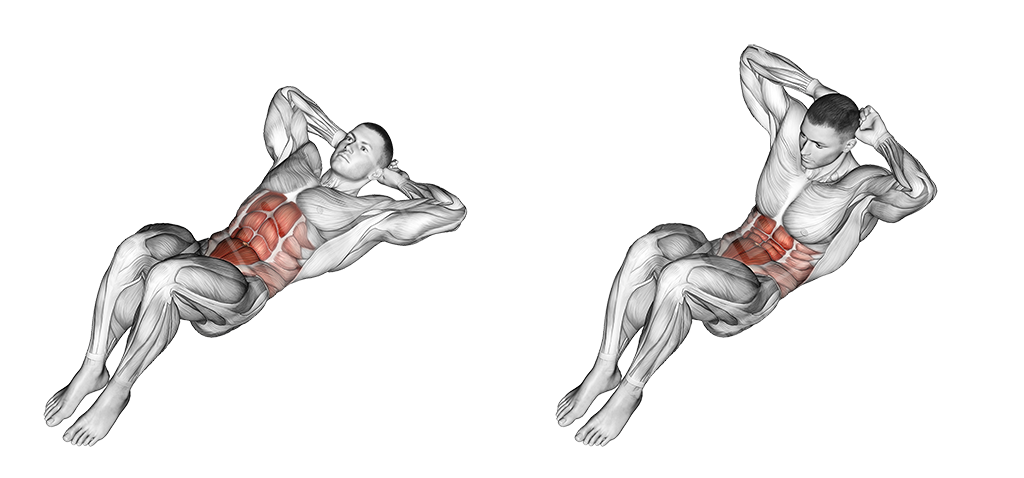

This is a basic abs exercise that will help you gain better control of your abdominal musculature and tone it up.
Execution
- Lay on the ground with your heels pulled in
- Place your hands behind your head
- Curl your torso, contracting the abs
Lower Back Hyper-Extension
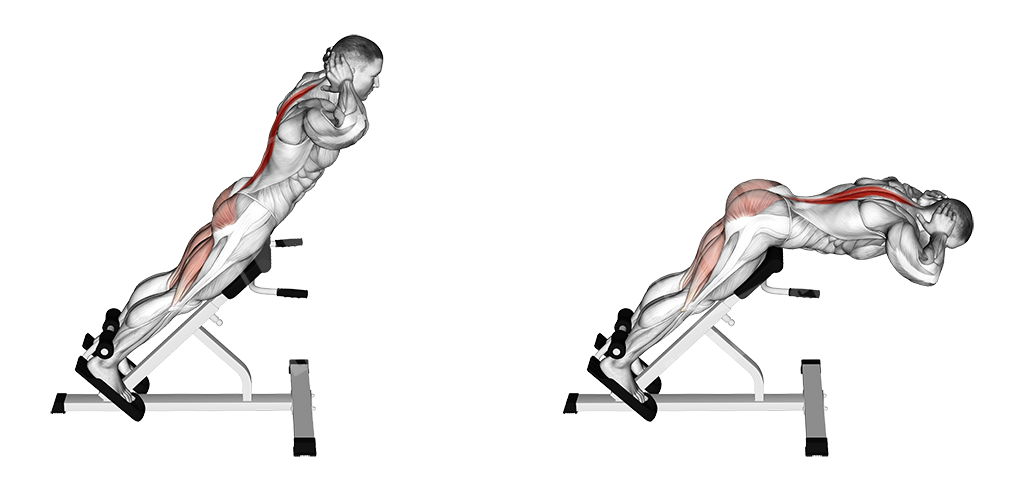

This exercise is done on the hyper-extension bench and helps you strengthen the long back muscles (spinal erectors)
Execution
- Get on the hyper-extension bench
- Place your hands behind your head
- Let your body go all the way down
- Go up, contracting your lower back musculature
Note
Keep a moderate pace and don’t overextend.
Exercise Showcase – Circuit (Full-Body) Workout #2
Incline Barbell Bench Press
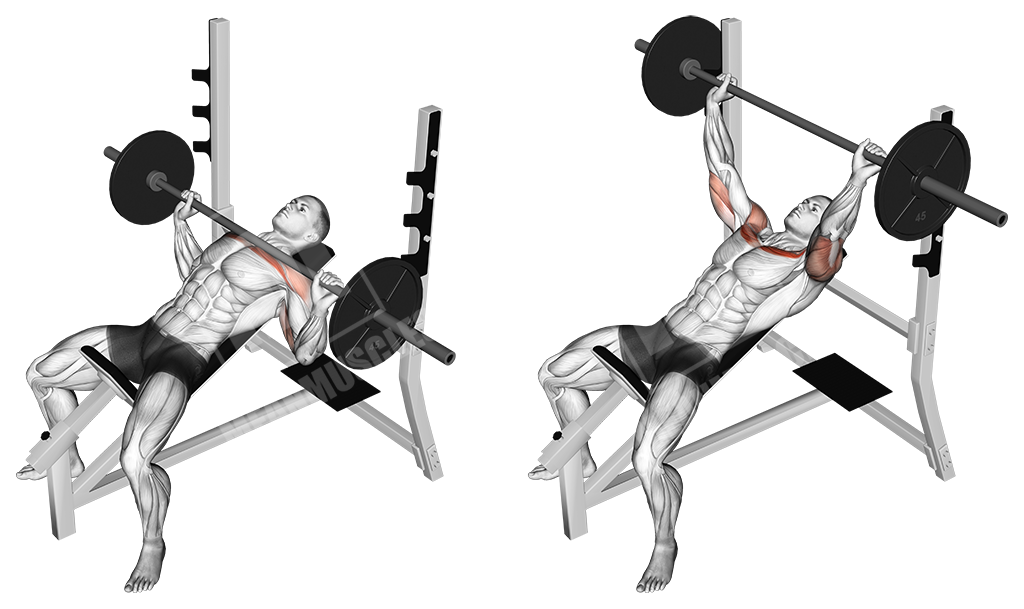

This is a variation of the pushing exercise ‘barbell bench press’, done on an incline bench, which allows the movement to target the upper portion of the chest musculature.
Execution
- Load the bar up with an appropriate weight
- Lay down on the bench and grab the bar slightly wider than shoulder width
- Un-rack the bar without locking out your elbows
- Let the bar down to the upper portion of your chest
- Push the weight up to the initial position
Note
Keep a moderate pace and constant tension on the chest.
Cable Seated Rows
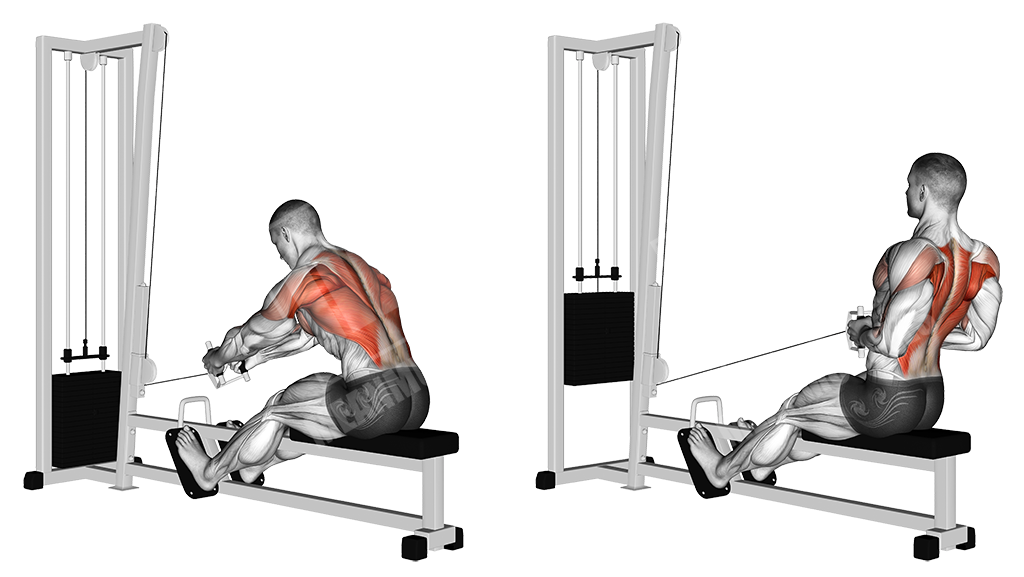

This is a basic cable exercise that will help you develop thickness in the back musculature, as well as the accompanying pulling strength development.
Execution
- Sit on the cable row machine and place your feet against the platform
- Grab the pulley and pull your torso back until it is at a 90-degree angle
- Let your arms and torso go forward, stretching the back, as illustrated
- Pull back, contracting the back musculature
Note
Keep your elbows close to the body.
Dumbbell Lateral Raise
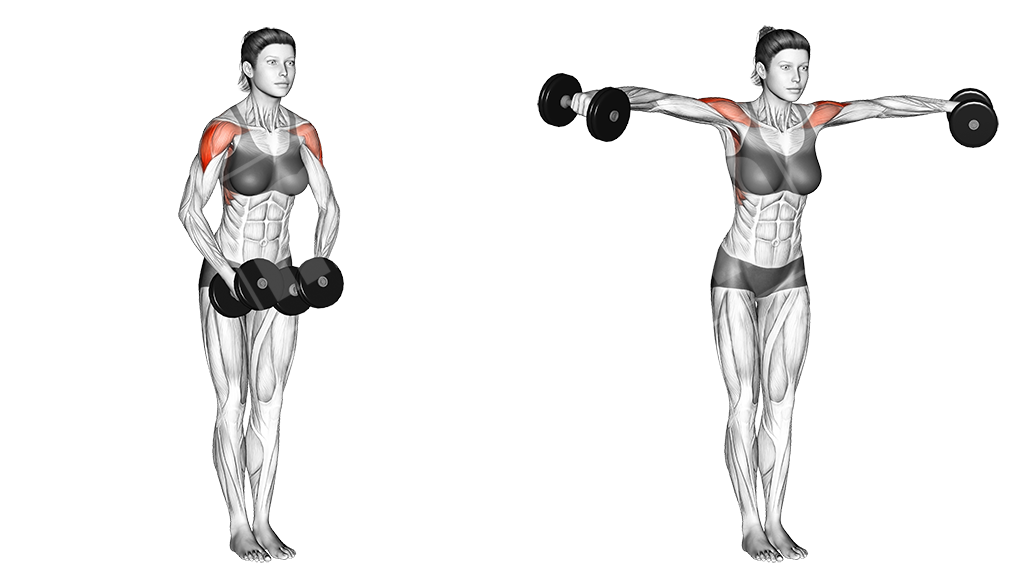

This is a basic unilateral dumbbell exercise, done separately or simultaneously with each arm. It primarily targets the side head of the deltoids, while also contracting the whole shoulder musculature.
Execution
- Pick an appropriate weight
- Stand up straight with the dumbbells by your sides
- Keep your elbows slightly bent
- Raise the dumbbells up, leading with your elbow and contracting the shoulders
- Hold the contraction for a split second and let the dumbbells down slowly
Note
Feel the deltoids contracting and keep constant tension on them.
EZ-Bar Bicep Curl
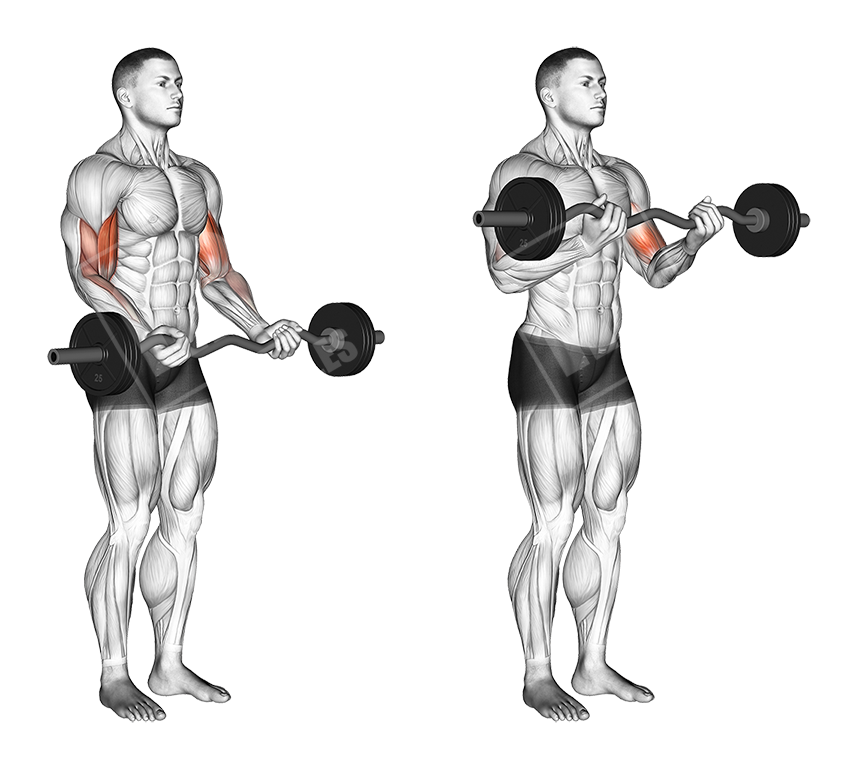

This is a basic curling movement, done with an EZ bar, that targets both heads of the biceps.
Execution
- Load the EZ-bar with an appropriate weight
- Pick the bar up with a grip that is at about shoulder width
- Curl the bar up, contracting the bicep
- Hold the contraction for a second and let the bar down slowly
Notes
- Do not swing the weight
- Keep your upper arm static to keep maximum tension on the biceps
- Do the exercise with moderate pace
Overhead Dumbbell Triceps Extensions
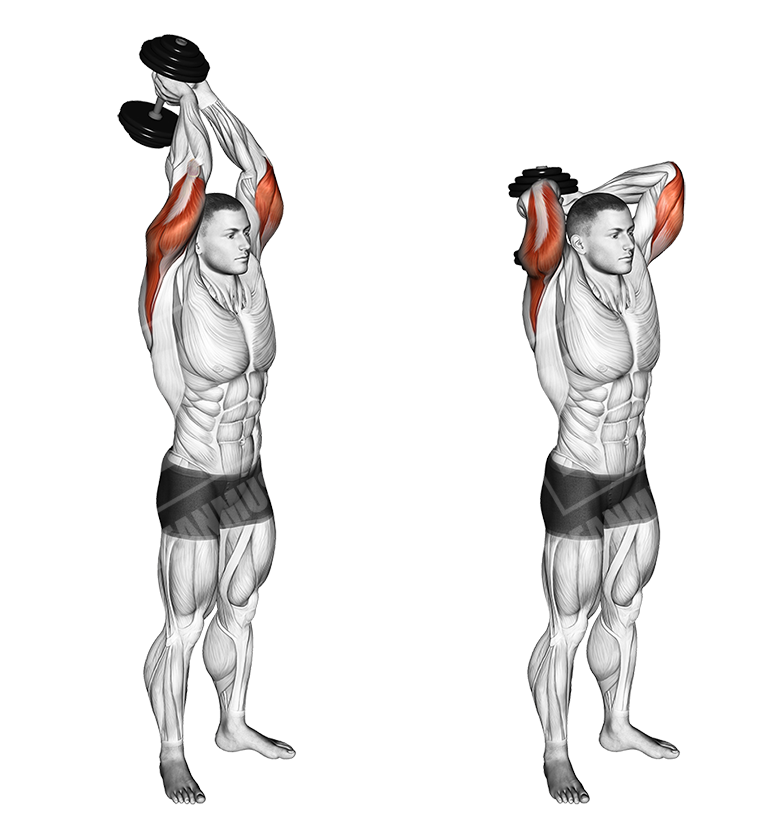


This is an isolated triceps movement, that will allow you to achieve higher mobility in the elbow joint, along with pushing strength and passive, isometric shoulder engagement, during the movement.
Execution
- Pick an appropriate weight
- Stand up with your feet at shoulder width to keep balance
- Get the dumbbell over your head, holding it with two hands
- Get your elbows closer to the head, with the arm being at a 90-degree angle
- Let the dumbbell down and behind your head
- Push the dumbbell up, contracting the triceps
Note
Do not aggressively lock out the elbows.
Sled Hack Squat
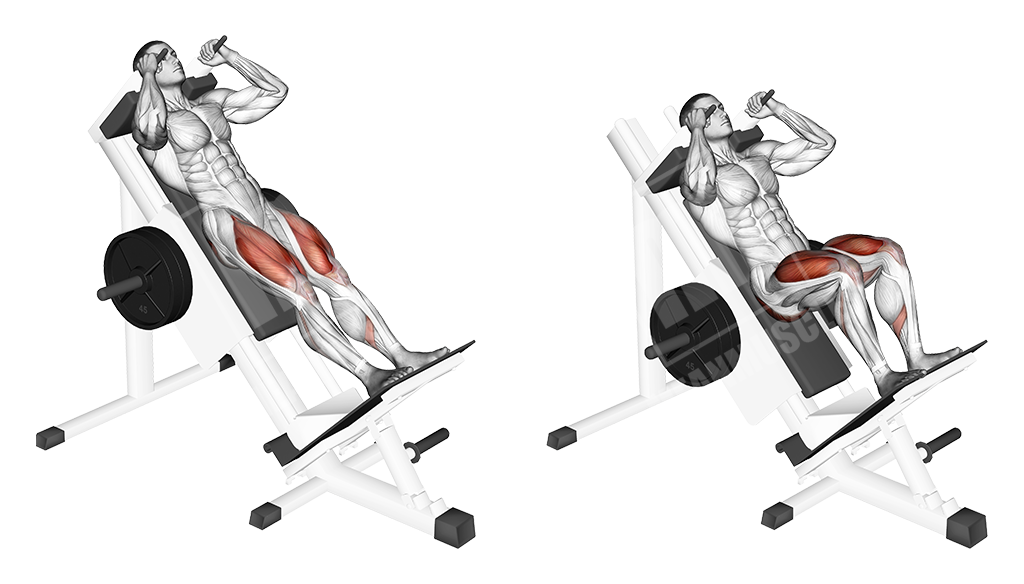


This is a basic, machine exercise that is basically a fixed-stance squat.
Execution
- Get on the sled
- Step with your feet at shoulder width or slightly wider, as you would in a normal squat
- Open your toes slightly
- Keep your back tight on the backrest
- Squat as low as you feel comfortable/able to do the exercise properly
Leg Press
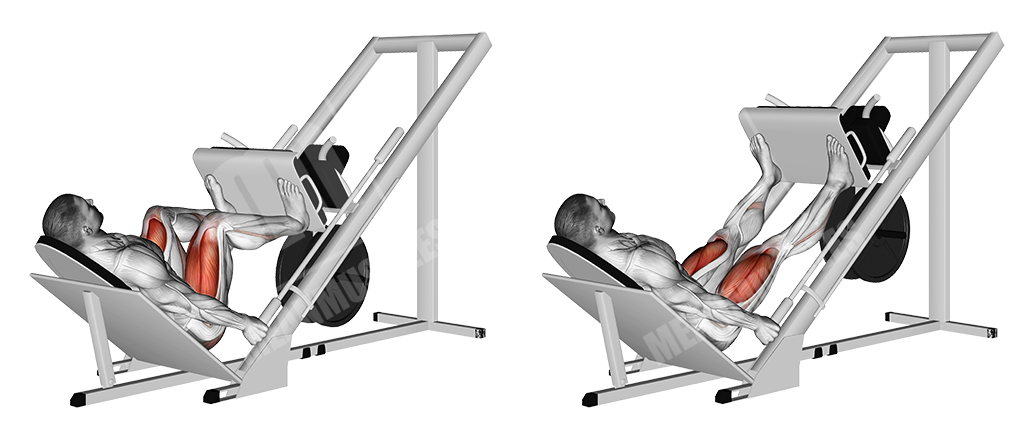

This is a basic machine lower body exercise that primarily targets the quadriceps and secondarily the hamstrings. It allows for a fixed movement and hence, constant tension.
Execution
- Lay down on the machine and make sure your lower back is stuck to the backrest
- Keep your head relaxed on the backrest as well
- Place your feet on the platform at shoulder width or slightly wider, with the toes being slightly opened up, just like in a squat stance.
- Make sure the toes are closer to the upper edge of the platform, especially if you are taller
- Un-rack the sled
- Keep knees slightly bent
- Let the sled go down, until the legs are at a 90-degree angle
- Push the sled up, contracting the quadriceps
Note
Do not lock the knees out, keep constant tension.
Seated Calf Machine Raises
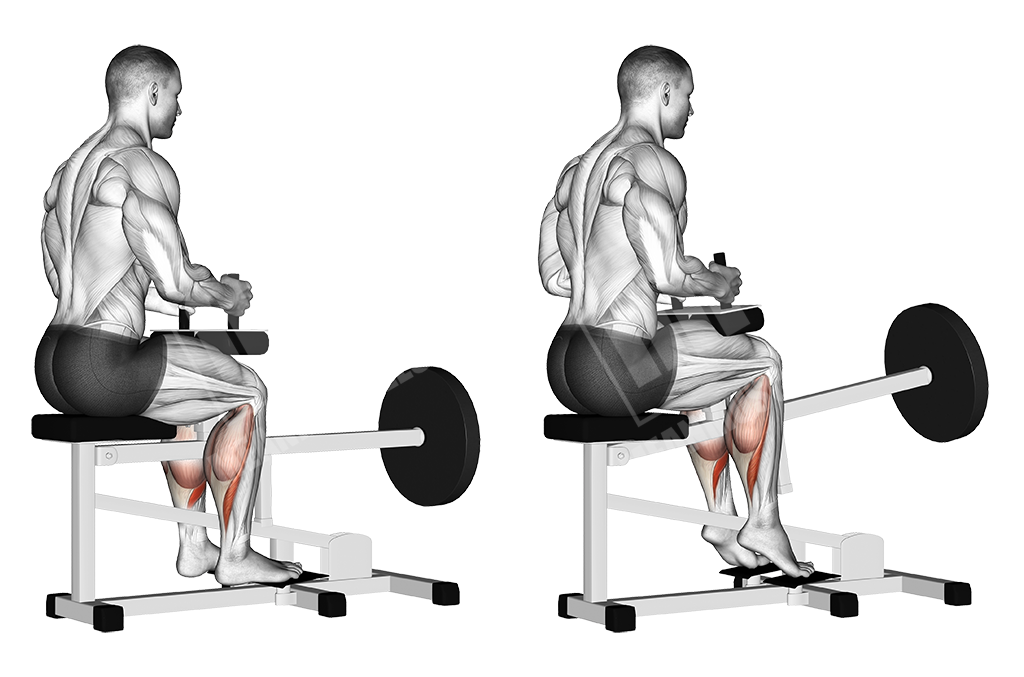

This is a basic calf movement, done from a seated position. This allows for the outer parts of the calf musculature to engage more in the movement.
Execution
- Sit on the calf machine
- Place your legs under the pads comfortably
- Step on the ledge with your toes
Standing Calf Raises
(Illustration and description available in circuit workout #1)
Lower Back Hyper-Extension
(Illustration and description available in circuit workout #1)
Cardio
Check out our Beginners’ Cardio article to find out the best approach to developing your cardio as a beginner.
Stretching
Check out our Stretching exercises section and Stretching Methods and Techniques article to find out the benefits of stretching, as well as some of the best stretching exercises for each body part.
Conclusion
Your goal as a beginner is to develop your strength, strength endurance and cardio endurance, through properly systemized, simple workout routines, that contain basic exercises.
Learning these exact basic exercises will allow you to optimally use your musculature during each movement, so keeping strict form of the exercise is important.
Learn the correct execution of each exercise, then start adding weights. We hope this guide has given you enough information on how to start working out.
Check out our Beginners’ Nutrition Guidelines to find out more about correct eating and sleeping habits. Together with a proper diet and a workout program, you can aim for weight loss and muscle building.


